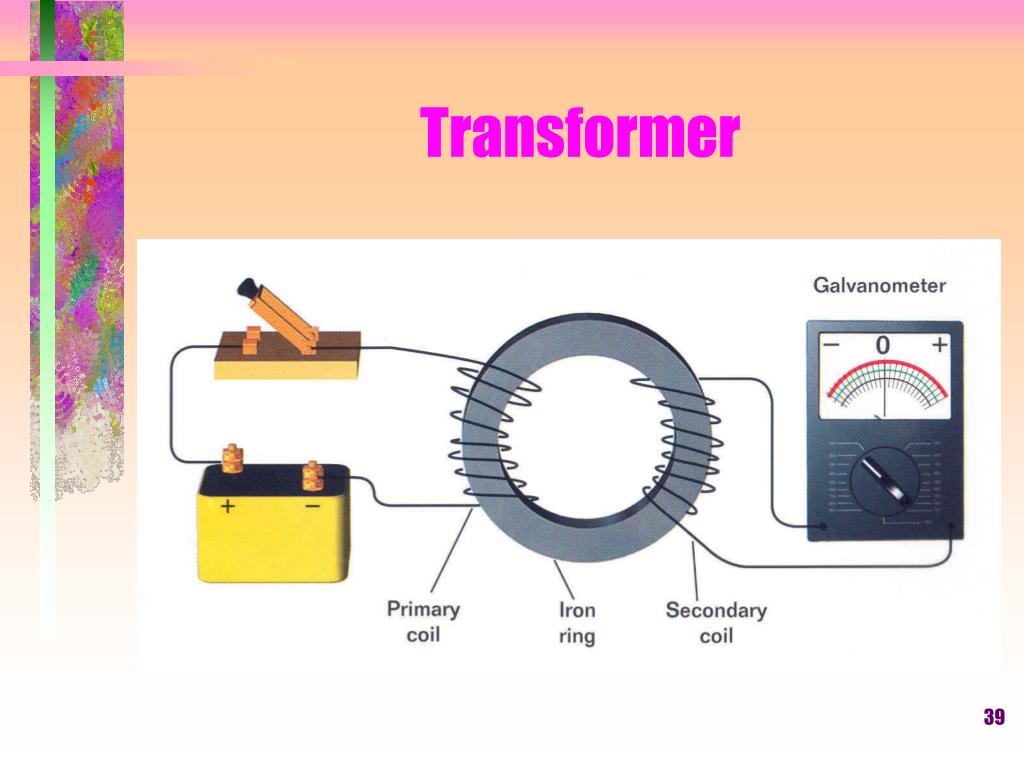
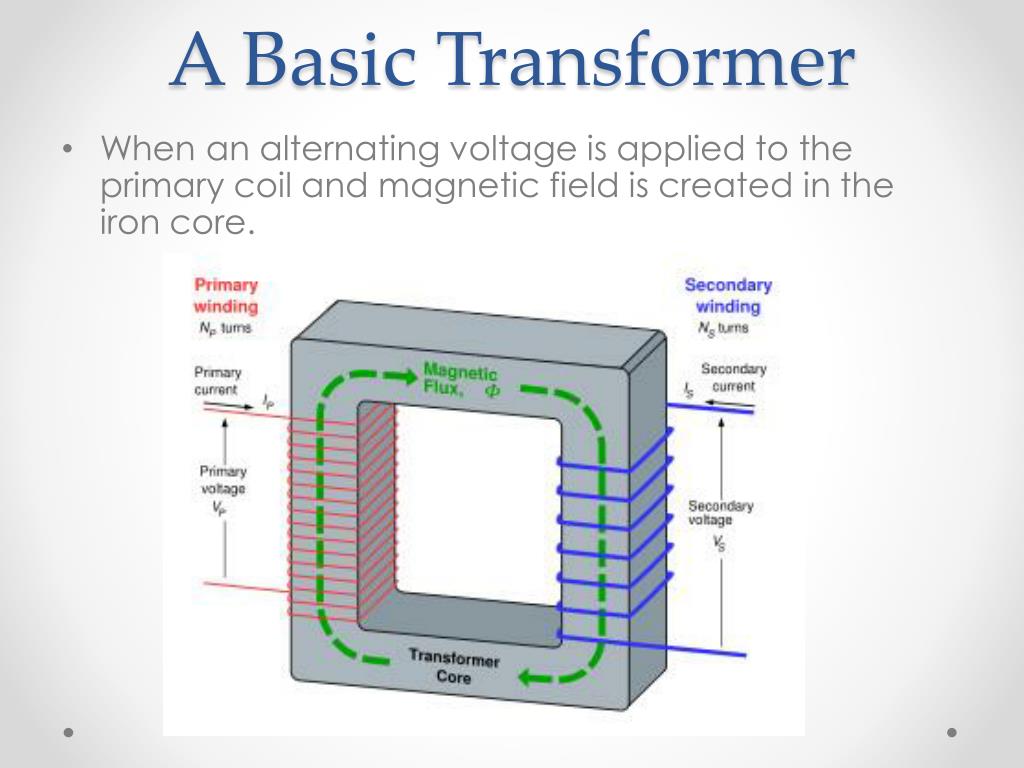
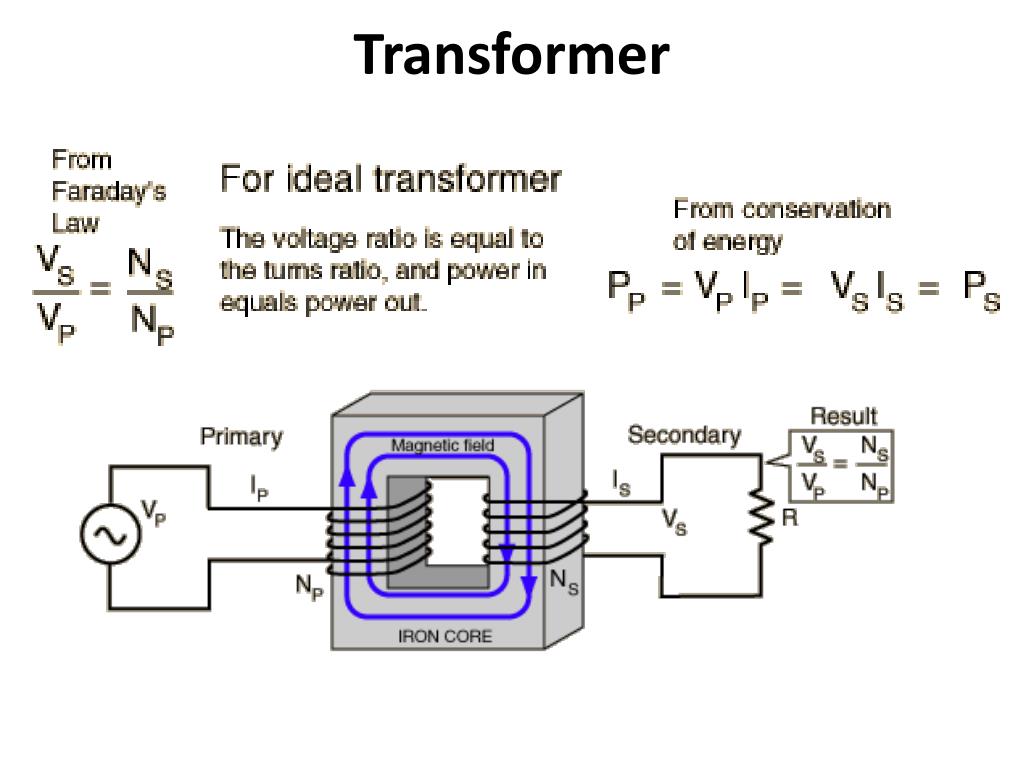
Figure 23.5.1: A transformer converts a primary alternating voltage, ∆ Vp, to a secondary alternating voltage, ∆ Vs. The magnetic flux produced in one coil is transmitted by an iron core to the secondary coil, where a different voltage is induced, depending on the ratio of the number of windings in each coil. The transformer has two coils.. A Transformer changes the voltage level (or current level) on its input winding to another value on its output winding using a magnetic field. A transformer consists of two electrically isolated coils and operates on Faraday's principal of "mutual induction", in which an EMF is induced in the transformers secondary coil by the magnetic.
PPT Field PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6592145

Transformer Working Principle Losses Efficiency Electrical A2Z
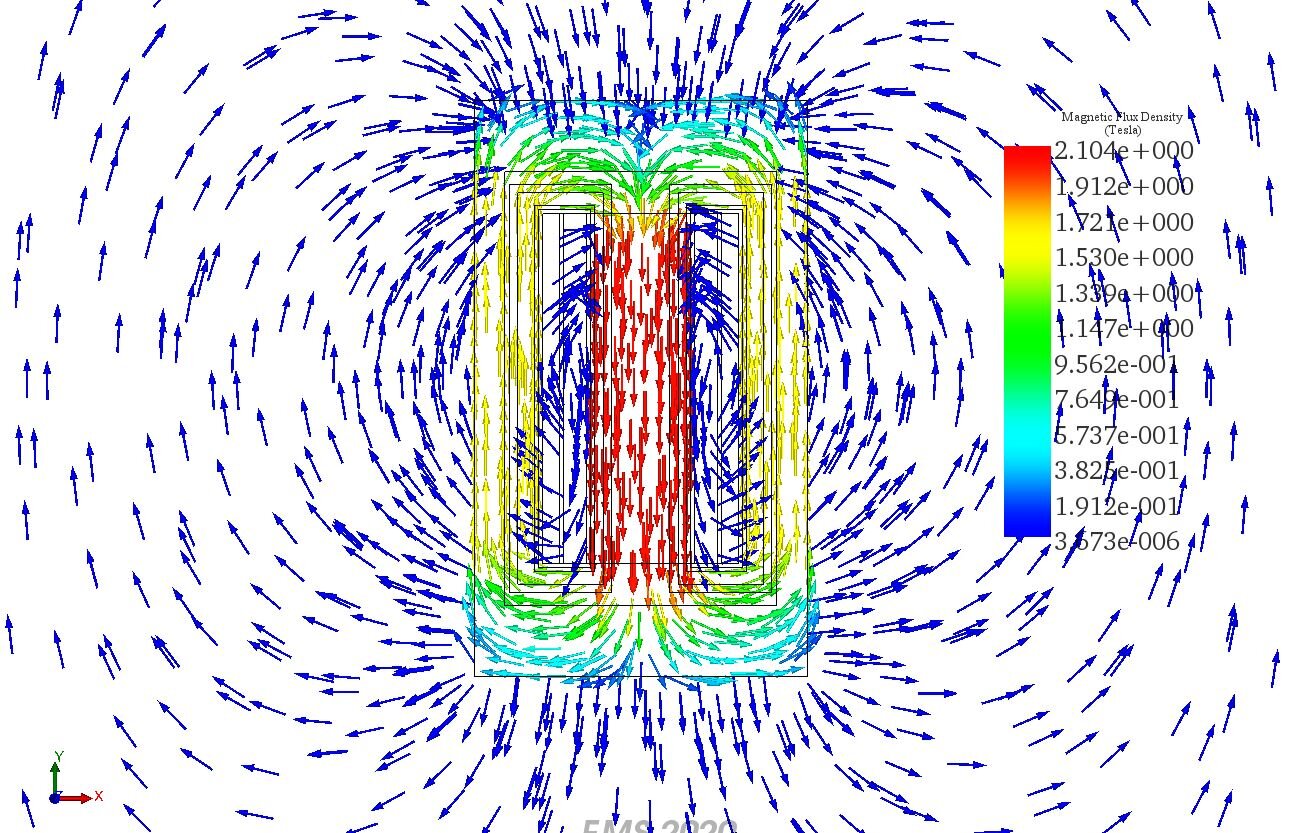
Singlephase transformer Coupling to Thermal Analysis in EMS
![Current in a Real transformer [PPT Powerpoint] Current in a Real transformer [PPT Powerpoint]](https://static.documents.pub/img/1200x630/reader012/image/20180207/56814f65550346895dbd19af.png?t=1626844407)
Current in a Real transformer [PPT Powerpoint]

field around AC transformer core, Active load 100W. YouTube
PPT Field Patterns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2813246
.7564ae5.jpg)
Transformer

Mutual inductance & transformers when EMF EMI
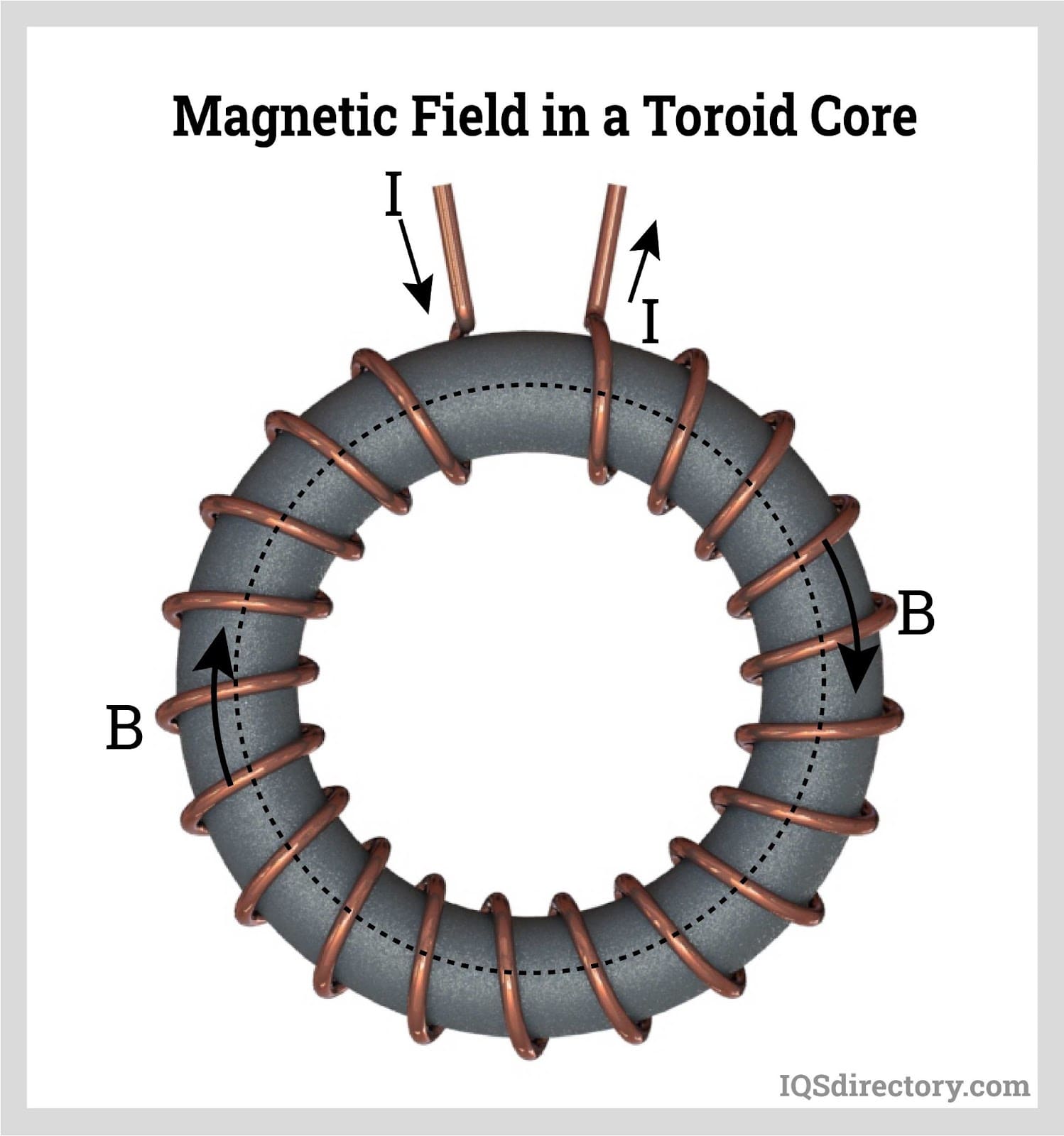
Toroidal Transformer What Is It? How Does It Work? Toroids

What is Leakage Flux and Fringing in Circuit ? Electrical Volt

iGCSE Physics Transformers YouTube
PPT Applied PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6599328

Circuits and Transformers 1 Fields 2

Fields, Effects, Variations Britannica
Monopole, Toroidal inductors and transformers, line Of Force, toroid,

Infinite EMF produced in transformer Physics Stack Exchange
EM 12 Fields 8 (Transformers) YouTube

Transformer Electric And Fields, Cliparts & Cartoons Jing.fm

induction Transformer and field/flux through the iron core? Physics Stack Exchange

field in the air gap of a transformer core Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange
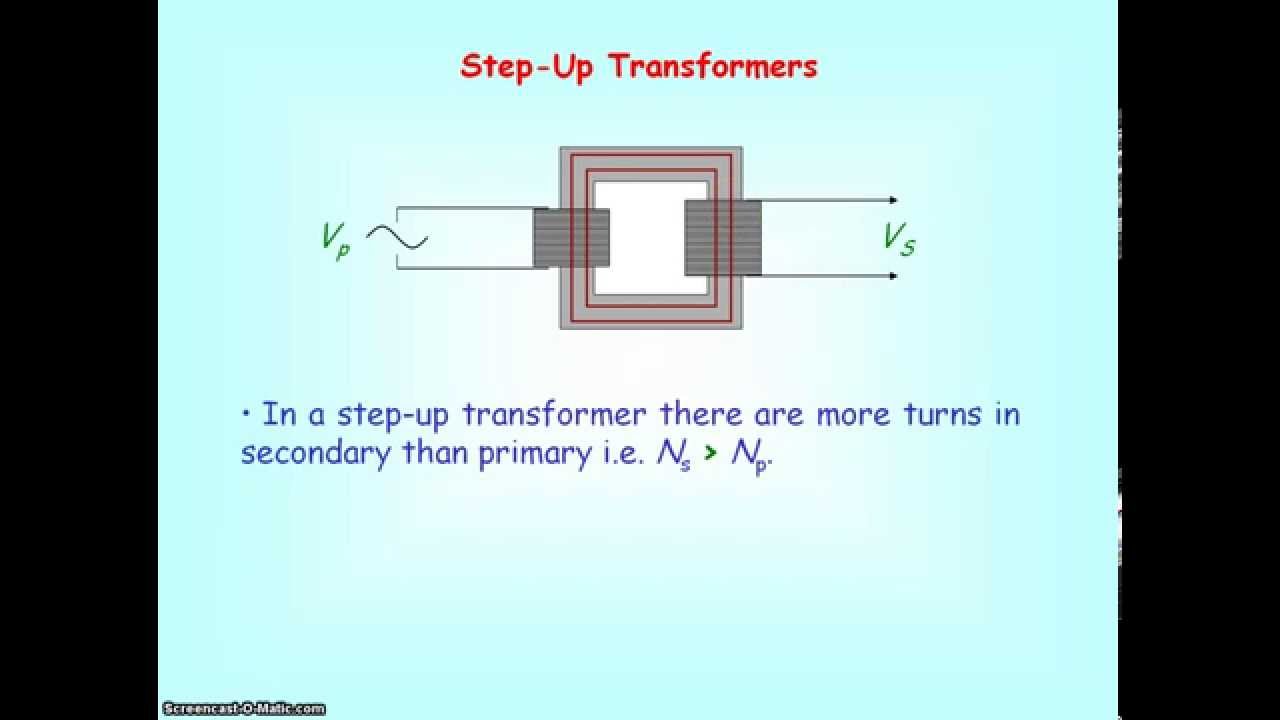
A transformer is a device that connects two electrical circuits through a shared magnetic field. Transformers are used in impedance transformation, voltage level conversion, circuit isolation, conversion between single-ended and differential signal modes, and other applications. 1 The underlying electromagnetic principle is Faraday's Law.. The following notation is used with a magnetic transformer: L1, L2: the self-inductance of the two coils. M: the mutual inductance. k: the coupling factor. k = M √L1L2. Referring to Figure 9.6.1 (e), the voltage transformer ratio is. V2 = nV1. where n is the ratio of the number of secondary to primary windings.